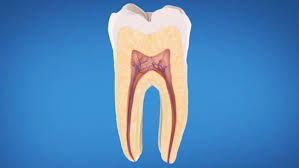
Cementum is a hard layer of tissue that helps the periodontal ligament attach firmly to a tooth. Made of cementoblasts, cementum slowly forms over a lifetime.
Cementum is a hard, calcified layer of tissue that covers the root of the tooth. On its outer side, cementum is attached to the periodontal ligament; on its inner side, the dentin. Along with the periodontal ligament, alveolar bone and gingiva, cementum helps a tooth stay in its place. In fact, if it weren’t for cementum, the periodontal ligament wouldn’t be able to attach firmly to a tooth.
Slowly formed throughout life, cementum is created when the root of the tooth excretes cementoblasts. Though cementoblasts are somewhat of a mystery, it is known that cementum is yellow in color and softer than dentin. Its chemical makeup is similar to that of bone — but unlike bone, cementum is avascular (not supported by blood vessels).
Types of Cementum
There are three types of cementum: acellular cementum, cellular cementum and afibrillar cementum. Acellular cementum covers about 1/3-1/2 of the root and has little to no cellular components. Cellular cementum covers about 1/3-1/2 of the apex and is permeable. Afibrillar cementum sometimes extends onto the enamel of the tooth.
If you have periodontal disease, your acellular cementum, cellular cementum or afibrillar cementum may also be diseased. A gum disease treatment called scaling and root planing can be performed to remove the diseased cementum, as well as dental tartar and diseased dentin.